Urinary Concerns / Incontinence
Urinary Issues
There are a handful of urinary issues you may encounter in your lifetime. Urinary issues can really take a toll on your quality of life as well as be disruptive and embarrassing. Women are twice as likely to suffer from urinary incontinence as men. Women are also more likely to suffer from urinary tract infections (UTIs) due to the location and short length of the urethra. The good news is you do not have to suffer through these uncomfortable symptoms.

Urinary Incontinence
SUI occurs when weakened muscles in the area cause a patient to leak urine when they cough, laugh, or sneeze, or when they perform exercises like walking or running.
Urgency Urinary Incontinence causes a patient to have a sudden strong urge to urinate, which is difficult to hold back. As a result, they may leak urine on the way to the bathroom or the bladder may empty completely before they reach the toilet.
Urinary Incontinence FAQs
In some cases, urinary incontinence is temporary due to a urinary tract infection, pregnancy, or certain medications. However, one of the most common causes of long-lasting urinary incontinence is a weakening of the muscles and tissues of the pelvic floor, usually because of aging or childbirth. In other cases, the symptom may be caused by anatomical obstructions, long-term constipation, menopausal hormonal changes, or hysterectomies in women. Neurological disorders can also cause urinary incontinence by disrupting the nerve signals to the muscles which control the bladder.
Kegel exercises, which strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor, can be helpful for some women with urinary incontinence. Overweight women will find that losing weight may reduce pressure on the pelvic area. Women may also benefit from limiting their intake of certain diuretic foods and beverages, like alcohol, coffee, and anything with caffeine. In the meantime, there are over-the-counter products available to contain leaked urine, which can relieve the social stress of urinary incontinence.
Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are highly common infections which occur when bacteria enters and grows inside part of the urinary tract, which includes the urethra, bladder, ureters, and kidneys.Most UTIs begin in the lower urinary tract (the bladder and urethra), but if the infection isn’t treated promptly, it can spread to the upper urinary tract as well (the ureters and kidneys), which can lead to more serious complications.
Women often develop UTIs from sexual activity, but the infection can also arise when the bladder does not empty completely due to a blockage or narrowing in the urinary tract. Symptoms often include a sharp pain or burning during urination, a frequent and urgent need to urinate, and soreness in the lower abdomen, back, or side, as well as urine with a strong odor, cloudy color, or small amounts of blood.
Urinary Tract Infection FAQs
UTIs may not be 100% preventable, but there are some steps you can take to minimize your risk:
- Always wipe from front to back (not back to front) after using the restroom.
- Keep the skin clean around the genital and anal area.
- Avoid using douches, powders, and deodorant sprays in the genital area.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Avoid holding in urine and fighting the urge to urinate.
- Try to empty your bladder before and after sex.
- Wear underwear with a cotton crotch.
- Avoid using spermicides or diaphragms and use other birth control methods instead
While UTIs are a rather minor health concern and can typically be cured quickly and easily, it’s important not to delay seeing your doctor at Gynecology Associates of Gwinnett. If left untreated, a UTI can spread to the upper urinary tract and cause a kidney infection, which could lead to long-term kidney damage and can even be life-threatening. It’s best to request an appointment as soon as you notice UTI symptoms but seek urgent medical care if you experience back pain, chills, fever, nausea, or vomiting, as these can be symptoms of a kidney infection.
For many patients,
the first recommendation will be one or more lifestyle changes. For those who are overweight, the excess weight can put additional pressure on the bladder and surrounding muscles, so weight loss can relieve enough of the pressure to make a significant difference. Adjusting your diet to avoid certain diuretics and limiting fluid intake at specific times may also be an option, and patients whose urinary incontinence is caused by weakened pelvic floor muscles may benefit from a specific type of exercise called Kegel exercises. However, if additional treatment is needed, options may include medication, devices like pessaries or urethral inserts, injections, or surgical procedures, depending on the hormonal or structural causes of the symptoms.
To start working toward freedom from your urinary incontinence, request an appointment at Gynecology Associates of Gwinnett.
Improve Your Pelvic Floor & Well-being
A non-invasive treatment for bladder control, leakage, and incontinence
Many people experience bladder control symptoms as they age. A weakened pelvic floor can cause symptoms like an uncontrolled sense of urgency or urinary incontinence.
This can add stress to your life and have a dramatic effect on your daily routine and hinder your sense of freedom. Our Emsella treatment at Gynecology Associates of Gwinnett can strengthen your pelvic floor to improve a variety of symptoms—all no downtime and no surgery.
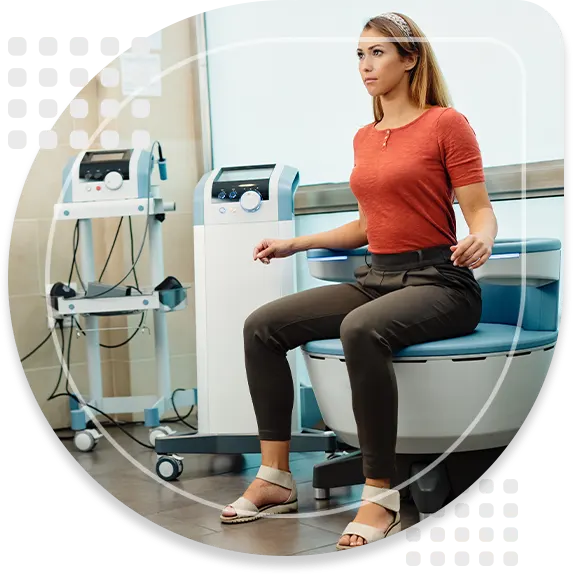

Treatment Highlights
-
Treatment Time:28 minutes
-
Recovery Period:None
Emsella works to help rehabilitate your pelvic floor muscles by stimulating thousands of muscle contractions. This treatment is fast, easy, and pain-free.
Treatable Conditions:
- Weak floor muscles
- Urinary leakage
- Urinary urgency
- Urinary frequency
How It Works
-
ConsultationBefore your Emsella treatment, you can meet with one of our providers at Gynecology Associates of Gwinnett for a complimentary consultation. We’ll ensure you are an ideal candidate, establish realistic expectations, and create a personalized treatment plan for you.
-
TreatmentThe treatment is very straightforward. You simply remain clothed and sit on the Emsella chair for the duration of the treatment. You will feel your pelvic floor muscles contract as it helps build strength in this area.
-
ResultsClients achieve the best results after multiple treatment sessions; we typically recommend a series of 6 treatments scheduled a few days apart.

Frequently Asked Questions
Get to Know More About Gynecology Associates of Gwinnett
Our goal at Gynecology Associates of Gwinnett is to give you an experience like no other to help you achieve personal wellness—beyond the scope of traditional medicine. We view our client relationships as partnerships, where clients feel involved and thoroughly enjoy the experience of working with us to pursue your goals.
You’re in the driver’s seat with us as your sidekick; we combine our expertise with your needs to achieve the best results possible with Emsella at Gynecology Associates of Gwinnett.

Find Your Perfect Treatment Match Today.
Contact Info
Our Hours
Monday: 8:30AM–4:30PM
Tuesday: 8:30AM–4:30PM
Wednesday: 8:30AM–4:30PM
Thursday: 8:30AM–4:30PM
Friday: 8:30AM–12PM
Quick Links
We Accept
Insurance & Self-Pay
Bill Pay

